Rac1 Regulates Neuronal Polarization through the WAVE Complex
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 17 novembro 2024

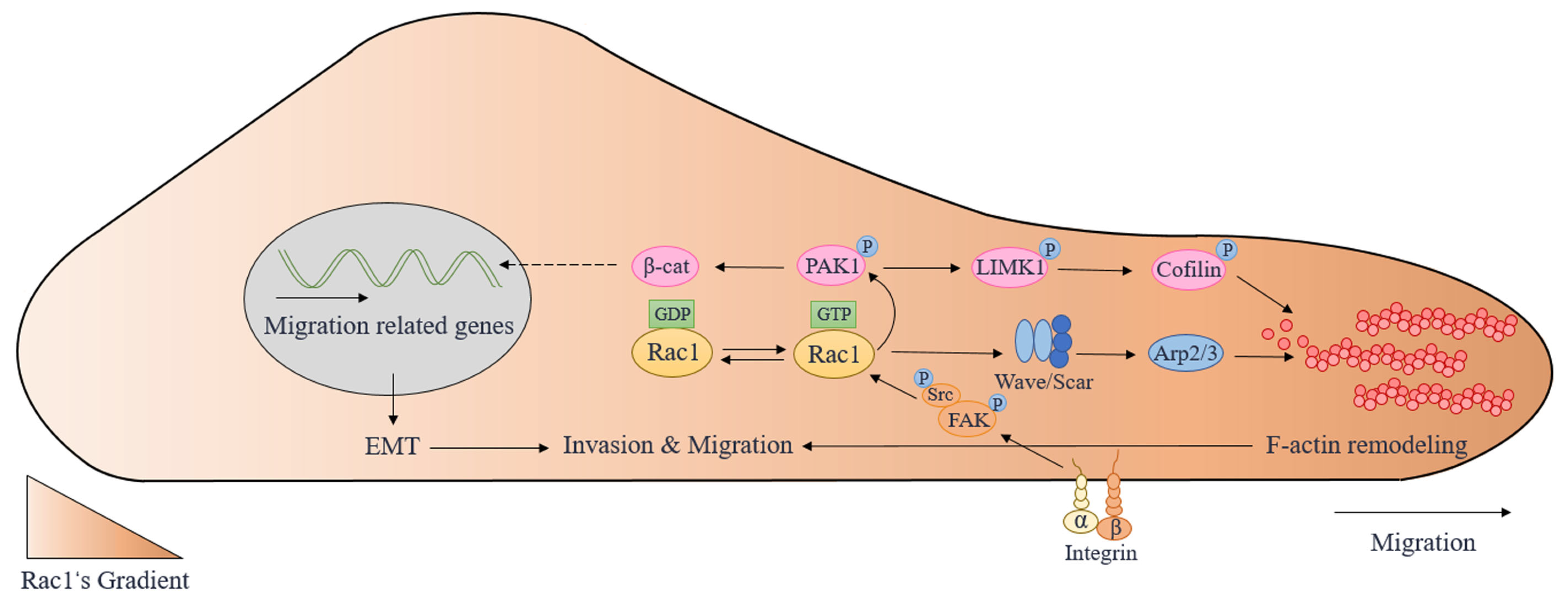
Neuronal migration and axon growth, key events during neuronal development, require distinct changes in the cytoskeleton. Although many molecular regulators of polarity have been identified and characterized, relatively little is known about their physiological role in this process. To study the physiological function of Rac1 in neuronal development, we have generated a conditional knock-out mouse, in which Rac1 is ablated in the whole brain. Rac1 -deficient cerebellar granule neurons, which do not express other Rac isoforms, showed impaired neuronal migration and axon formation both in vivo and in vitro . In addition, Rac1 ablation disrupts lamellipodia formation in growth cones. The analysis of Rac1 effectors revealed the absence of the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family verprolin-homologous protein (WAVE) complex from the plasma membrane of knock-out growth cones. Loss of WAVE function inhibited axon growth, whereas overexpression of a membrane-tethered WAVE mutant partially rescued axon growth in Rac1 -knock-out neurons. In addition, pharmacological inhibition of the WAVE complex effector Arp2/3 also reduced axon growth. We propose that Rac1 recruits the WAVE complex to the plasma membrane to enable actin remodeling necessary for axon growth.

Neuronal Polarity: Positive and Negative Feedback Signals. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Effect of Rac1 inhibition on actin polarization in dendritic filopodia.

Rac1 drives melanoblast organization during mouse development by orchestrating pseudopod- driven motility and cell-cycle progression. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Molecules, Free Full-Text
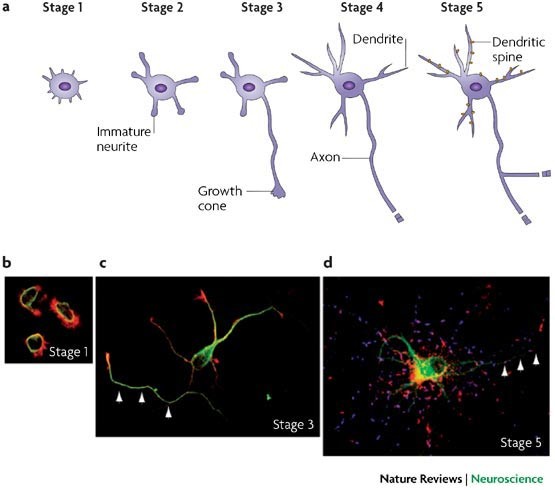
Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms
PDF) Rac1 Regulates Neuronal Polarization through the WAVE Complex

MAP1B Regulates Axonal Development by Modulating Rho-GTPase Rac1 Activity

Local changes in microtubule network mobility instruct neuronal polarization and axon specification

CYRI (FAM49) proteins are local inhibitors of Scar/WAVE induced lamellipodia that bind directly to active Rac1

Rac1 Controls the Formation of Midline Commissures and the Competency of Tangential Migration in Ventral Telencephalic Neurons
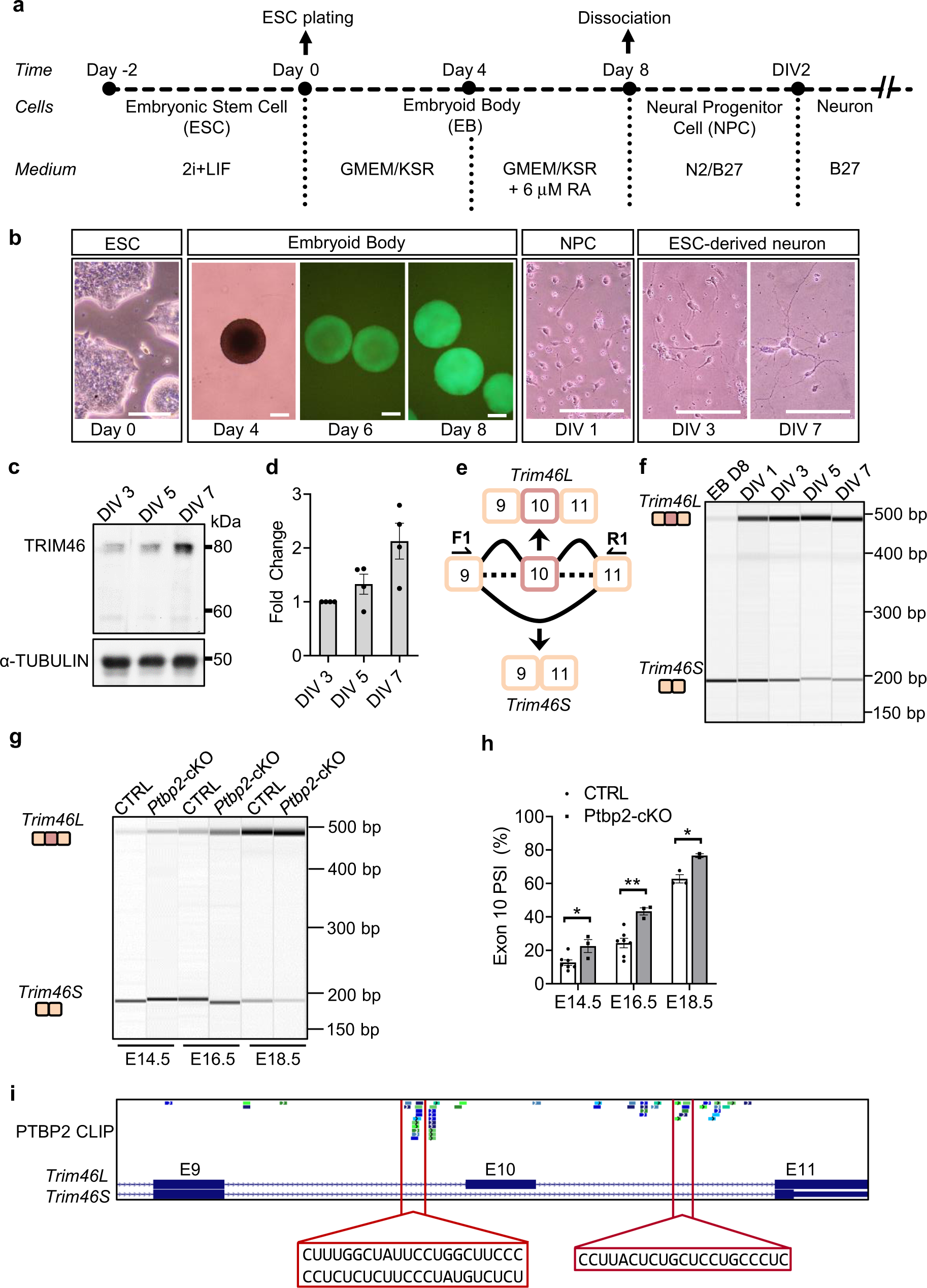
Multilayered regulations of alternative splicing, NMD, and protein stability control temporal induction and tissue-specific expression of TRIM46 during axon formation
Recomendado para você
-
 Waveigl MBTI Personality Type: ESTJ or ESTP?17 novembro 2024
Waveigl MBTI Personality Type: ESTJ or ESTP?17 novembro 2024 -
 Achei wave igl na academia OF I / ELE TILT - iFunny Brazil17 novembro 2024
Achei wave igl na academia OF I / ELE TILT - iFunny Brazil17 novembro 2024 -
 IGL says oxygen supplies adequate for fourth COVID wave, Lead Stories17 novembro 2024
IGL says oxygen supplies adequate for fourth COVID wave, Lead Stories17 novembro 2024 -
Marcos Santos - Proprietário da Wave Idiomas / Imersão Inglês Fluente - Wave Idiomas / Imersão Inglês Fluente17 novembro 2024
-
 JBL Wave Flex Fone de ouvido TWS17 novembro 2024
JBL Wave Flex Fone de ouvido TWS17 novembro 2024 -
 Isso é Black Belt, csgo inteligente. - waveigl17 novembro 2024
Isso é Black Belt, csgo inteligente. - waveigl17 novembro 2024 -
 Prepared to Surf - oferece versão em inglês17 novembro 2024
Prepared to Surf - oferece versão em inglês17 novembro 2024 -
 Seahorse Wave Necklace Pendant Blue Topaz Paua Abalone17 novembro 2024
Seahorse Wave Necklace Pendant Blue Topaz Paua Abalone17 novembro 2024 -
 Mario Kart 8 Deluxe – Booster Course Pass Wave 2 coming 4th August - My Nintendo News17 novembro 2024
Mario Kart 8 Deluxe – Booster Course Pass Wave 2 coming 4th August - My Nintendo News17 novembro 2024 -
 Bitxe Rotxa (main beach) in Porto Inglês - Discover Cape Verde17 novembro 2024
Bitxe Rotxa (main beach) in Porto Inglês - Discover Cape Verde17 novembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Juan Pablo Gamboa Influencer Profile - Work With Influencer Juan17 novembro 2024
Juan Pablo Gamboa Influencer Profile - Work With Influencer Juan17 novembro 2024 -
 Real Madrid usa 'barreira de robôs' para treinar cobranças de falta; assista17 novembro 2024
Real Madrid usa 'barreira de robôs' para treinar cobranças de falta; assista17 novembro 2024 -
 Demon Slayer: 2ª temporada do anime ganha novo trailer; assista17 novembro 2024
Demon Slayer: 2ª temporada do anime ganha novo trailer; assista17 novembro 2024 -
Chess 2d - Pieces Position 2 - Openclipart17 novembro 2024
-
 Samehadaku Lewat Link Nonton Anime Isekai Meikyuu de Harem wo Episode 8 Bahasa Indonesia Disini Bukan Gomunime17 novembro 2024
Samehadaku Lewat Link Nonton Anime Isekai Meikyuu de Harem wo Episode 8 Bahasa Indonesia Disini Bukan Gomunime17 novembro 2024 -
 Mera Mera No Mi, One Piece Prime Wiki17 novembro 2024
Mera Mera No Mi, One Piece Prime Wiki17 novembro 2024 -
Hasbro Transformers Studio Series Voyager Class Megatron 8.5-in17 novembro 2024
-
 Tamataki & Chamataki Garten of Banban 3 Plush Toys Soft Stuffed Plushie Garden17 novembro 2024
Tamataki & Chamataki Garten of Banban 3 Plush Toys Soft Stuffed Plushie Garden17 novembro 2024 -
Elton John - Sacrifice #lyricsright17 novembro 2024
-
 THE KING OF FIGHTERS 98 Easy Combo Edition MUGEN ANDROID - All Super Max Moves 202317 novembro 2024
THE KING OF FIGHTERS 98 Easy Combo Edition MUGEN ANDROID - All Super Max Moves 202317 novembro 2024